Posts Tagged: science
I am a postdoc and I think I just realized I have been screwed for years
It seems in the past two weeks someone has started going around lifting big stones in the luxurious and exotic garden of science, finding the obvious gross underneath. To be more precise, the topic being discussed here is: “I am a postdoc and I think I just realized I have been screwed for years“.
A couple of weeks ago, a friend of mine blogged about his decision to leave academia after yet another nervous breakdown. I leave it to his words to describe what it means to realize in your early thirties that your childhood dream won’t become a reality because the job market is broken and you can’t cope with that stress. To be honest, while I sympathize with him, I find his rant extreme, but what is more important than discussing anecdotal experiences is actually the huge number of comments that post had, not only on the blog but also on social discussion websites. Literally hundreds of comments from people who went through similar experiences, culminating with the epiphany that finding a job in academia is freaking difficult.
This discussion is not new, of course. Occasionally people from academia feel the urge to let postdocs and PhD student know that this is a very risky road. See Jonathan Katz’s opinion from back in 2005, for instance.
Why am I (a tenured professor of physics) trying to discourage you from following a career path which was successful for me? Because times have changed (I received my Ph.D. in 1973, and tenure in 1976). […] American universities train roughly twice as many Ph.D.s as there are jobs for them. When something, or someone, is a glut on the market, the price drops. In the case of Ph.D. scientists, the reduction in price takes the form of many years spent in “holding pattern” postdoctoral jobs. Permanent jobs don’t pay much less than they used to, but instead of obtaining a real job two years after the Ph.D. (as was typical 25 years ago) most young scientists spend five, ten, or more years as postdocs. They have no prospect of permanent employment and often must obtain a new postdoctoral position and move every two years.
Pretty actual, isn’t it? Although these arguments do emerge now and then, they do it way less than they should¹. Why? The main reason is that PIs have really nothing to gain from changing the current situation: as it is now, they find the field overcrowded with postdocs who cannot do anything else but staying in the lab, hoping to get more papers than their competitors; waiting for the unlucky ones to drop out to reduce competition. That means it’s easy for the PIs to get postdocs for cheap and keep them in the lab as long as possible.
Of course there could be an even better scenario for PIs: postdocs who never leave the lab! Let’s face it: having so many postdocs to choose from is nice, but many of them aren’t actually that good and also it takes time for them to acquire certain skills. So why don’t give them the chance to stay for 20 years in the same lab? This is exactly what Jennifer Rohn was advocating on Nature last week. I think in her editorial Jennifer actually rightly identifies the problem:
The system needs only one replacement per lab-head position, but over the course of a 30–40-year career, a typical biologist will train dozens of suitable candidates for the position. The academic opportunities for a mature postdoc some ten years after completing his or her PhD are few and far between.
But she fails to provide the right solution:
An alternative career structure within science that professionalizes mature postdocs would be better. Permanent research staff positions could be generated and filled with talented and experienced postdocs who do not want to, or cannot, lead a research team — a job that, after all, requires a different skill set. Every academic lab could employ a few of these staff along with a reduced number of trainees. Although the permanent staff would cost more, there would be fewer needed: a researcher with 10–20 years experience is probably at least twice as efficient as a green trainee.
I cannot even start saying how full of rage this attitude makes me. This position is so despicable to me! Postdoc positions exist, on the first place, because they provide a buffer for all those who would like to get a professor job but cannot, due to the limited market. Any economist would tell you that the solution is not to transform this market into something even more static but to increase mobility, for Newton’s sake! Sure, some postdocs may realize too late they don’t really want to be independent and they would gladly keep doing what they are doing for some more time: this is what positions in industry are for², and this is what a lab tech position is for. No need to invent new names for those jobs.
So, here I propose an alternative solution: what about giving postdocs the chance of being independent, without necessarily being bound to running a 4 people lab to start with, or without the need to hold a tenure position? What about redistributing resources so that current PIs will have a smaller lab so that 1 or 2 more people somewhere else could have the chance to start their own career? Isn’t this more fair?
I wrote about this before, so I won’t repeat myself: in short, the big lab model is not sustainable anymore and it is not fair!
The problem, Jennifer, is not that postdoc want to stay longer in the lab: the problem is that they want out!
Notes
1: a recurrent question in the new Open Science society is “should scientists be blogging?“. My answer is yes, definitely (in fact, that’s what I am doing) but I don’t expect them to blog about their opinion on the last paper in their field. I don’t think that is so useful, actually. I’d rather have them talk about their daily life as scientists and speak freely and loudly about controversial issue.
2: My wife is one of them: she realized she didn’t want to have anything to do with academia anymore and she moved to industry where she actually got a salary that was more than twice the one she was getting in the University doing pretty much the same job, without worrying about fellowships and competition. She has never been so happy at work, too.
What has changed in science and what must change.
I frequently have discussions about funding in Science (who doesn’t?) but I realized I never really formalized my ideas about it. It makes sense to do that here. A caveat before I start is that everything I write about here concerns the field of bio/medical sciences for those are the ones I know. Other fields may work in different ways. YMMV.
First of all, I think it is worth noticing that this is an extremely hot topic, yet not really controversial among scientists. No matter whom you talk to, not only does everyone agree that the status quo is completely inadequate but there also seem to be a consensus on what kind of things need to be done and how. In particular, everyone agrees that
- more funding is needed
- the current ways of distributing funding and measuring performance are less than optimal
When everybody agrees on what has to be done but things are not changing it means the problem is bigger than you’d think. In this post I will try to dig deeper into those two points, uncovering aspects which, in my opinion, are even more fundamental and controversial.
Do we really need more funding?
The short answer is yes but the long answer is no. Here is the paradox explained. Science has changed dramatically in the past 100, 50 (or even 10) years, mainly because it advances at a speedier pace than anything else in human history and simply enough we were (and are) not ready for this. This is not entirely our fault since, by definition, every huge scientific breakthrough comes as a utter surprise and we cannot help but be unprepared to its consequences¹. We did adapt to some of the changes but we did it badly and we did not do it for all to many aspects we had to. In short, everyone is aware about the revolution science has had in the past decades, yet no one has ever heard of a similar revolution in the way science is done.
A clear example of something we didn’t change but we should is the fundamental structure of Universities. In fact, that didn’t change much in the past 1000 years if you think about it. Universities still juggle between teaching and research and it is still mainly the same people who does both. This is a huge mistake. Everybody knows those things have nothing in common and there is no reason whatsoever for them to lie under the same roof. Most skilled researchers are awful teachers and viceversa and we really have no reason to assume it should not be this way Few institutions in the world concentrate fully on research or only teaching but this should not be the exception, it should be the rule. Separating teaching and research should be the first step to really be able to understand the problems and allocate resources.
Tenure must also be completely reconsidered. Tenure was initially introduced as a way to guarantee academic freedom of speech and action. It was an incentive for thoughtful people to take a position on controversial issues and raise new ones. It does not serve this role anymore: you will get sacked if you claim something too controversial (see Lawrence Summers’ case) and your lab will not receive money if you are working on something too exotic or heretic. Now, I am not saying this is a good or a bad thing. I am just observing that the original meaning of tenure is gone. Freedom of speech is something that should be guaranteed to everyone, not just academic, through constitutional laws and freedom of research is not guaranteed by tenure anyway because you don’t get money to do research from your university, you just get your salary. It’s not 1600 anymore, folks.
Who is benefiting from tenure nowadays? Mainly people who have no other meaning of paying their own salary, that is researchers who are not active or poorly productive and feel no obligation to do so because they will get their salary at the end of the month anyway. This is the majority of academic people not only in certain less developed countries – like Italy, sigh – but pretty much everywhere. Even in the US or UK or Germany many departments are filled with people who publish badly or scarcely. Maybe they were good once, or maybe it was easier at their time to get a job. Who pays for their priviledge? The younger generation, of course.
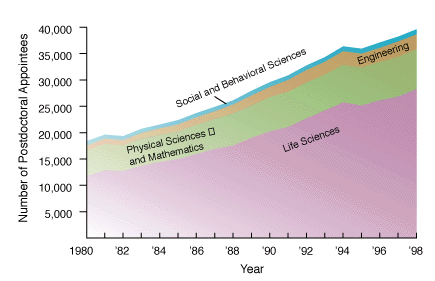
The number of people entering science grows every year², especially in the life sciences. The number of academic position and the funding extent is far from being sufficient to cover current needs. In fact, about 1-2 in 10 postdoc will manage to find a job as professor and among those who do, funding success rate is again 20-30% in a good year. In short, even if we were to increase the scientific budget by 5 times tomorrow morning that would still not be enough. This means that even though it would be sure nice to have more money, it’s utopia to think this will help. Indeed, we need to revolutionize everything, really. People who have tenure should not count on it anymore and they should be ready to leave their job to somebody else. There is no other way, sorry.
Do we really need better forms of scientific measurement?
No. We need completely new forms of scientific measurement. And we need to change the structure of the lab. Your average successful lab is composed of 10 to 30 members, most of them PhD students or postdocs. They are the ones who do the work, without doubts. In many cases, they are the ones who do the entire work not only without their boss, but even despite the boss. This extreme eventuality is not the rule, of course, but the problem is: there is no way to tell it apart! The principal investigator as they say in the USA, or the group leader as it is called with less hypocrisy in Europe, will spend all of their time writing grants to be funded, speaking at conferences about work they didn’t do, writing or merely signing papers. Of course leading a group takes some rare skills, but those are not the skill of a scientist they are the skills of a manager. The system as it is does not reward good scientists, it rewards good managers. You can exploit creativity of the people working for you and be succesful enough to keep receiving money and be recognized as a leader but you are feeding a rotten process. Labs keep growing in size because postdocs don’t have a chance to start their own lab and because their boss uses their work to keep getting the money their postdoc should be getting instead. This is an evil loop.
This is a problem that scientometrics cannot really solve because it’s difficult enough to grasp the importance of a certain discovery, let alone the actual intellectual contribution behind it. It would help to rank laboratories not just by number of good publications, but by ratio between good papers and number of lab members. If you have 1 good paper every second year and you work alone, you should be funded more than someone who has 4 high publications every year but has a group of 30 people.
Some funding agencies, like HHMI, MRC and recently WellcomeTrust, decided to jump the scientometric problem and fund groups independently of their research interest: they say “if you prove to be exceptionally good, we give you loads of money and trust your judgement”. While this is a commendable approach, I would love to see how those labs would rank when you account for number of people: a well funded lab will attract the best sutudents and postdocs and good lab members make a lab well funded. Here you go with an evil loop again.
In gg-land, the imaginary nation I am supreme emperor of, you can have a big lab but you must really prove you deserve it. Also, there are no postdocs as we know them. Labs have students who learn what it means to do science. After those 3-5 years either you are ready to take the leap and do your stuff by yourself or you’ll never be ready anyway. Don’t kid yourself. Creativity is not something you can gain with experience; if at all, it’s the other way around: the older you get, the less creative you’ll be.
Some good places had either a tradition (LMB, Bell labs) or have the ambition (Janelia) of keeping group small and do science the way it should be done. Again, this should not be the exception. It should be the rule. I salute with extreme interest the proliferation of junior research fellowships also known as independent postdoc positions. They are not just my model of how you do a postdoc. In fact they are my model of how you do science tout court. Another fun thing about doing science with less resource is that you really have to think more than twice about what you need and spend your money more wisely. Think of the difference between buying your own bike or building one from scratch. You may start pedaling first if you buy one, but only in the second case you will have a chance to build a bike that run faster and better. On the long run, you may well win the race (of course you should never reinvent the wheel; it’s OK to buy those).
Of course, the big advantage of having many small labs over few big is that you get to fund different approaches too. As our grandmother used to say: it’s not good to keep all eggs in the same basket. As it happens in evolution, you have to diversify, in science too³.
What can we (scientists) do? Bad news is, I don’t think these are problems that can be solved by scientists. You cannot expect unproductive tenure holders to give up their job. You cannot expect a young group leader to say no to tenure, now that they are almost there. You cannot expect a big lab to agree in reducing the number of people. Sure, all of them complaint that they spend their times writing grants and cannot do the thing they love the most – experiments! – anymore because too busy. If you were to give them the chance to go back to the bench again, they would prove as useless as an undergrad. They are not scientists anymore, they are managers. These are problem that only funding agencies can solve, pushed by those who have no other choice that asking for a revolution, i.e.: the younger generation.
Notes:
1. Surprise is, I believe, the major difference between science and technology. The man on the moon is technology and we didn’t get there by surprise. Penicillin is science and comes out of the blue, pretty much.
2. Figure is taken from Mervis, Science 2000. More recent data on the NSF website, here.
3. See Michael Nielsen’s post about this basic concept of life.
Update:
Both Massimo Sandal and Bjoern Brembs wrote a post in reply to this, raising some interesting points. My replies are in their blogs as comments.